Meningioma Surgery and Treatment in India
Plan your Meningioma Surgery and Treatment in India with Dheeraj Bojwani Consultants
Meningioma Surgery and Treatment in India are done at the accredited medical facilities by the internationally trained and qualified health care professionals. Dheeraj Bojwani Consultants is a premier medical tourism company in India offering services of the most sought-after surgeons to the international patients, at affordable rates in India.
How things function at Dheeraj Bojwani Consultants
- Excellent panel : Patients are guided and assisted to choose the treatment most suitable for them, under the #1 specialists in India.
- Primary facilities : We take care the most important facets like appointment with doctors, your medical visa, accommodation, healthy meals.
- Recovery assistance : You may have to stay in the hospital for 2 to 3 days post treatment depending on your surgery. Dheeraj Bojwani Consultants will help you in your speedy recovery.
- Low cost : The cost involved in the parathyroid tumor surgery in India, your stay, flight tickets, meals etc is nearly 25% of the expenses in western countries.
- Other services : Quick visa letter, flight ticket bookings, languators, foreign exchange facility, hotel arrangement, vacation tours and plans.
What is Meningioma?
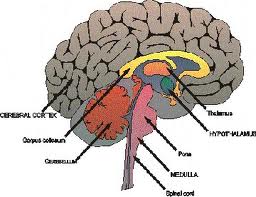 Meningioma is a type of tumor that develops from the meninges, the membrane that covers the brain and spinal cord. There are three layers of meninges, called the dura mater, arachnoid and pia mater. Most meningiomas (90%) are categorized as benign tumors (non-cancerous), with the remaining 10% being a typical or malignant. However, Benign tumours can cause significant injury, can be life threatening and can be extremely difficult to treat.
Meningioma is a type of tumor that develops from the meninges, the membrane that covers the brain and spinal cord. There are three layers of meninges, called the dura mater, arachnoid and pia mater. Most meningiomas (90%) are categorized as benign tumors (non-cancerous), with the remaining 10% being a typical or malignant. However, Benign tumours can cause significant injury, can be life threatening and can be extremely difficult to treat.
In many cases, benign meningiomas grow slowly. This means that depending upon its location a meningioma may grow relatively large in size before it causes symptoms. Other meningiomas grow more rapidly, or have sudden growth spurts. There is no way to predict the rate of growth for a meningioma, or to know for certain how long a specific tumor was growing before diagnosis.
Most people with a meningioma will only have a tumor at only one site, but it is also possible to have several tumors growing simultaneously in different parts of the brain and spinal cord. When multiple meningiomas occur, more than one type of treatment may have to be used.
A primary brain tumor originates in the central nervous system, while metastatic brain tumors spread to the brain from other parts of the body. Meningiomas account for about 27% of primary brain tumors, making them the most common of that type.
Types of Meningioma
The WHO's (World Health Organization) classification scheme recognizes 15 variations of meningioma according to their cell type as seen under the microscope. These variations are called meningioma subtypes. WHO graded each of these meningioma subtypes into one of three categories based primarily upon the likelihood of recurrence and the rate of growth exhibited by each. A higher tumor grade is associated with a greater likelihood of the tumor’s recurrence and/or faster growth rate and increased potential of brain invasion (often referred to as more aggressive behavior).
Benign (Grade I): Approximately 90% of all meningiomas fall into the benign category. These tumors exhibit slow growth and very little multiplication of cells and very rarely invade the brain tissue. Overall, benign meningiomas are less likely to recur than the atypical and malignant grades. Meningiothelial, Fibrous (fibroblastic), Transitional (mixed), Psammomatous, Angiomatous, Microcystic, Secretory, Lymphoplasmacyte-rich and Metaplastic are subtypes of Grade I.
Atypical (Grade II): Atypical meningiomas represent approximately 7-8% of meningiomas and exhibit increased tissue and cell abnormalities. These tumors exhibit a faster growth rate than benign meningiomas and, on occasion, some degree of brain invasion. Atypical meningiomas have a higher likelihood of recurrence than benign. Chordoid, Clear Cell and Atypical are subtypes of Grade II.
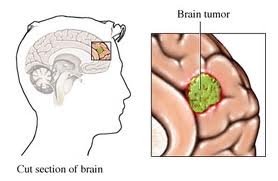 Meningioma Surgery and Treatment in India Malignant (Grade III): Malignant meningiomas account for approximately 2-3% of all meningiomas. These tumors show increased cellular abnormalities as well as a faster growth rate compared to benign and atypical meningiomas. Malignant meningiomas are the most likely to invade the brain and spread (metastasize) to other organs in the body. Of the three types, they are the most likely to recur. Papillary, Rhabdoid and Anaplastic are subtypes of Grade III.
Meningioma Surgery and Treatment in India Malignant (Grade III): Malignant meningiomas account for approximately 2-3% of all meningiomas. These tumors show increased cellular abnormalities as well as a faster growth rate compared to benign and atypical meningiomas. Malignant meningiomas are the most likely to invade the brain and spread (metastasize) to other organs in the body. Of the three types, they are the most likely to recur. Papillary, Rhabdoid and Anaplastic are subtypes of Grade III.
Causes of Meningioma
Causes of Meningioma are not clear. It is believed that something changes the cells in the membranes that form a protective barrier around your brain and spinal cord. These changes make them multiply uncontrollably, leading to a meningioma tumor. But it remains unknown whether this is caused by genetic factors, environmental factors or a combination of both.
Some potential causes are as follows
Ionizing Radiation: The radiation used in medicine that creates ions by knocking electrons out of atoms. Ions penetrate and interfere with living tissue, causing tumor cells to die as they attempt to reproduce. Exposure to ionizing radiation has been found to be associated with a higher incidence of intracranial tumors and particularly meningiomas.
Hormones: An association between meningiomas and hormones has been suggested by a number of findings, including: the increased incidence of these tumors in women versus men; the presence of hormone receptors such as estrogen, progesterone, and androgen on some meningiomas; an association between breast cancer and meningiomas; and indications that meningiomas increase in size during the menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
Genetic: Meningiomas may arise from highly penetrant, but relatively rare inherited genes. These genes are primarily observed in families with neurofibromatosis 2 (Nf2).
Trauma: Meningiomas have been found at the site of previous traumas such as head injuries, but the relationship is not fully understood.
Cell Phone Use: The question of cell phone use and the exposure to electromagnetic fields remains of interest to the public as potential cause of meningiomas and other brain tumors.
Viruses: There is a possibility that viruses may be related to meningioma formation but that relationship is not defined.
Who is at risk?
Meningiomas are most common in people between the ages of 40 and 70. They are more common in women than in men. Among middle-aged patients, there is a marked female bias, with a female: male ratio of almost 3:1 in the brain and up to 6:1 in the spinal cord. Meningiomas are very rare in children, with pediatric cases accounting for only 1.5% of the total.
click here
Phone Numbers Reach Us-
India & International : +91-9860755000 / +91-9371136499
UK : +44-2081332571
Canada & USA : +1-4155992537
Symptoms of Meningioma:
The types of symptoms that patients with meningiomas experience include seizures, headaches, muscle weakness, confusion, and changes in personality, visual disorders and hearing loss. Seizures are the most common symptom associated with cranial meningiomas, appearing in 30 to 40% of patients pre-treatment.
Examples of tumor effects associated with specific locations are presented in the following table.
Falx and parasagittal: Symptoms can vary depending upon the location of these tumors along the falx, a groove that runs between the brain’s two hemispheres in a front to back direction. For example, those located in the frontal section may impair higher levels of brain functioning such as reasoning and memory, while those located in the middle section would be more likely to cause leg weakness.
Convexity: Seizures, headaches and neurological deficits related to the specific location of the tumor on the surface of the brain.
Sphenoid wing (also called sphenoid ridge): Problems with vision, loss of sensation in the face, or facial numbness, and seizures.
Olfactory groove: Loss of smell due to compression of the nerves that run between the brain and the nose, and if the tumor grows big enough, visual symptoms can be expressed due to compression of the optic nerve.
Suprasellar: Problems with vision due to compression of the optic nerve.
Posterior fossa: Facial symptoms or loss of hearing due to compression of cranial nerves.
Intraventricular: May block the flow of cerebrospinal fluid causing pressure to build up (obstructive hydrocephalus), which can produce headaches, wooziness, and changes in mental function.
Intraorbital: Buildup of pressure in the eyes, giving a bulging appearance and potential loss of vision.
Spinal: Back pain, or pain in the limbs, from compression of the nerves where they run into the spinal cord.
Diagnosis of Meningioma
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans effectively detect most meningiomas and are best at displaying details of the brain.
Sometimes a CT scan is obtained to evaluate whether there is any bone (skull) involvement, or if the tumor is calcified.
Treatment of Meningioma:
Treatment of a meningioma is often done in stages, depending on the size and location of the tumor. Treatments can include observation, surgery and radiation.
Observation/ Conservative Management for Meningioma
If a meningioma is very small and causing few, if any, symptoms, physicians may choose to simply monitor the tumor over time. Observation with regularly scheduled MRI scans (see Diagnostic Procedures) is usually the only action necessary.
Surgery for Meningioma
 Meningioma surgery varies from relatively straightforward to highly complex, sometimes requiring multiple surgeons from different specialties. The ease of removal depends upon both their accessibility and the skill of the neurosurgeon.
Meningioma surgery varies from relatively straightforward to highly complex, sometimes requiring multiple surgeons from different specialties. The ease of removal depends upon both their accessibility and the skill of the neurosurgeon.
Endovascular Neurosurgery: Tumors rely on blood supplies that feed their growth and allow tumor cells to multiply. Endovascular neurosurgery techniques cut off these blood supplies (also known as embolization) before surgery. This helps to make actual neurosurgery much safer, makes removing the tumor easier and lowers the risk of significant blood loss.
- Endoscopic removal of meningiomas through the nose. This surgery is appropriate for tumors at the base of the skull or upper spine.
- Keyhole microsurgical removal using eyebrow incision
- Endoport removal is a minimally invasive option for meningiomas located within the ventricles (fluid spaces). A narrow tube or port allows doctors to access the tumor through a tiny incision in the skull, in contrast to conventional brain surgery.
Radiation Therapy for Meningioma:
Patient who are ineligible for surgery or who had incomplete surgical removal, conventional radiosurgery and/or steriotactic radiosurgery can be used to slow or stop the growth of meningiomas.
Radiation treatment is often considered for deep, surgically inaccessible tumors, or tumors in elderly patients. Patients who are less than 50 years of age need to be counselled about the risk of developing radiation-induced cancer 10 or more years after radiation treatment. Fortunately, the chances of this happening appear to be very small.
Meningiomas have sharp margins and rarely invade neighboring tissue, thus they are ideal tumors for focused, shaped radiation fields using the Novalis Shaped-Beam Surgery.
This technique does not require actual surgery, but instead uses advanced imaging and computer technology to deliver a high dose of radiation to the tumor while limiting radiation exposure to the surrounding brain structures.
For many meningioma tumors, the radiation field needs to be conformed to the shape of the tumor. In addition, delivering the radiation in smaller doses over a period of weeks will reduce the risk of injuring critical brain structures next to the tumor (which may cause blindness, deafness, paralysis). Some treatment techniques, such as the Gamma Knife, cannot deliver this type of treatment.
Chemotherapy, Hormone Therapy and Immunotherapy:
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill tumor cells. Hormone therapies are of interest because of the fact that hormones seem to play a possible role in some meningiomas and immunotherapy uses drugs that help the body’s immune system to control tumor growth. These treatments often are called systemic treatments because the drug or agent is distributed on a system-wide basis throughout the body and not to just one specific location. These therapies have not been widely used for treatment of meningiomas and their level of success to date has been limited. They are most often tried with recurrent, malignant, or inoperable tumors, and in some instances appear to slow the growth of the tumor and prolong the patient’s life. Surgery and/or radiation therapy are still the primary choice of treatment.
Benefits of Treatment and Surgery of Meningioma:
Surgical resection has been the standard treatment for meningiomas for more than two generations and has many specific advantages. Most importantly, if the meningioma can be completely resected, and is confirmed to be benign, the cure rate is very high. The prognosis following meningioma treatment is very good.
Spinal meningioma is the most successfully treated meningioma, and the most successfully treated of all spinal tumors. Most of these tumors are removed completely, and they rarely recur. Most medical centers report excellent tumor control rates (90-95%) after radiosurgery. The risk of neurologic injury depends on location. For the few patients who are inoperable (usually because of tumor location), radiation therapy can stop the growth of tumors. If patients have clinical symptoms, such as headaches, double vision, seizures, etc; there is a significant likelihood that these will improve after radiosurgery.
Fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery (FSR) makes it possible to more safely treat some larger meningiomas, or those immediately next to critical structures, like the vision (optic) nerve.
This procedure uses images of the patient's skull to construct a frame that allows precise aiming of radiation, thus minimizing harm to nearby healthy tissue.
Meningioma Treatment and Surgery in India
 India has emerged as a prime destination for medical tourists from around the world. The services range from executive health packages to complicated surgeries. People are attracted towards the superior quality in healthcare, accredited medical facilities, and internationally trained and qualified health care professionals and travel to India for their health care needs. The level of healthcare services in the leading hospitals and medical centers of India are ‘on par’ to what is being offered in US and UK.
India has emerged as a prime destination for medical tourists from around the world. The services range from executive health packages to complicated surgeries. People are attracted towards the superior quality in healthcare, accredited medical facilities, and internationally trained and qualified health care professionals and travel to India for their health care needs. The level of healthcare services in the leading hospitals and medical centers of India are ‘on par’ to what is being offered in US and UK.
India offers several hospitals and medical centers that are known widely for its best medical and health care services in wide variety of specialty fields. It has a pool of experienced and skilled neurosurgeons that specialise in complex and challenging brain tumour surgery like most Meningioma. The hospitals and health care professionals of India have patient-centered attitude. India hospitals have revolutionary technology and most methods of treating Meningioma. The physician and surgeon handle many cases every day and have acquired a skill in operating different difficult and complicated surgeries.
Cities in India where one can find best centers providing Meningioma treatment and surgery are as follows:
| Mumbai | Hyderabad | Kerala |
| Delhi | Pune | Goa |
| Bangalore | Nagpur | Jaipur |
| Chennai | Gurgaon | Chandigarh |
Patient from Malaysia – Ms. Damia Megat shares her Mother's experience of Meningioma Surgery in India

Ms. Damia and her mother Ms. Sophia Megat from Malaysia
Surgeries related to brain are probably the most dangerous and complicated ones. When my mother was diagnosed with meningioma and her neurosurgeon recommended an immediate surgical treatment to prevent the tumor from spreading in other parts of the brain, we were really worried about the risks involved because the survival rates in such chances are half and half always. But the doctors and staff at Dheeraj Bojwani groups was really supportive throughout the procedure. They ensured that we were made aware of every complication involved and they gave us hope that there is a probability of having a successful surgery in the case of my mother.
★★★★★ Published
Low cost Meningioma Treatment and Surgery in India
India is known not only for the best medical and health services it offers but also for the economical cost of these medical services. This attracts millions of people every year from US, UK and other developed countries. This has made India the most attractive medical tourist destination of the world. The total cost including consultation fee, hospital stay, medicine, surgery, accommodation, transportation, etc can save around 60-80% of the healthcare seeker. The low cost does not make the facilities and the quality of services any less important. There is absolutely no compromise on quality. Low cost treatment and surgery of Meningioma in India has benefited many patients from all across the globe. Radiation therapy provides a cost saving of an estimated 50-70%.
click here
Phone Numbers Reach Us-
India & International : +91-9860755000 / +91-9371136499
UK : +44-2081332571
Canada & USA : +1-4155992537
Some of the common countries from which patients travel to India for surgery are:
| USA | UK | Canada |
| Australia | New Zealand | Nigeria |
| Kenya | Ethiopia | Uganda |
| Tanzania | Zambia | Congo |
| Sri Lanka | Bangladesh | Pakistan |
| Afghanistan | Nepal | Uzbekistan |
 Apollo Hospital
Apollo Hospital Fortis Hospital
Fortis Hospital Artemis Hospital
Artemis Hospital Max Hospital
Max Hospital Columbia Asia Hospital
Columbia Asia Hospital Medanta Hospital
Medanta Hospital


 Jaslok Hospital
Jaslok Hospital Lilavati Hospital
Lilavati Hospital


 Global Hospitals
Global Hospitals